UNIX is earliest and most widely used network Operation system.
It is available is many versions like Sun Solaris, HP, UNIX, AIX UNIX, and BSD. Though developed for different hardware platforms they all have similar networking features.
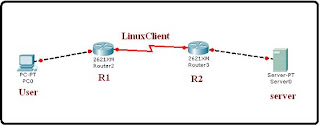
LINUX SYSTEM
Linux is an open Source networking Operation System based on UNIX architecture.
Linux provide flexibility to users for altering it according to there individual requirements.
Feature of Linux / UNIX
Security: it supports different levels of access permission for each user file and directory. So unauthorized user can not access a file beyond a certain specified level.
Linux/Unix it treaded all the device treated as files.
It is provide Internet based service like mail, web browsing and transfer
Different protocol has been support FTP, SMTP, HTTP,HTTPS
 |